1. General information about pneumatic vibrators
This manual contains information on two types of pneumatic vibrators
• Vibrators with radial vibration (balls, rollers or turbines)
• Vibrators with linear vibration (piston)
1.2. Basic information about pneumatically driven vibrators
1.2.1. What is vibration used for?
With the help of vibration, any kind of bulk material can be conveyed, compacted or separated. In most cases, vibration supports the force of gravity.Arises material bridges or materials adhesions in bunkers or funnels due to humidity e.g. - vibrations may loosen the material, and the gravitational force continue to convey the material.A further application of pneumatic vibrators e.g. is compacting of concrete. Concrete with its contained particles of sand and gravels is reduced to a compact volume by vibration – without any inclusions of air.In both cases vibration reduces the friction of the material.
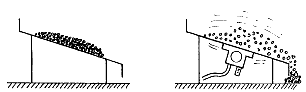
Vibration and gravitation
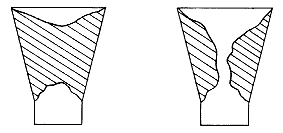
No formation of material bridges and adhesion of materials by using pneumatic vibration
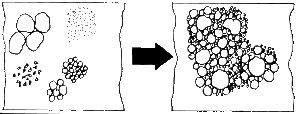
Compacting concrete
Pneumatic vibrations do not necessarily increase the force of gravity. Vibrations just allow the material to "jump". Gravity ensures the return of the material on the strainer or the channel.
Using linear vibrators allows to determine the direction of the material “jump”. By adjusting the amplitude, the length of the jump can be variegated. Rotary vibrators such as ball, roller or turbine vibrators can also be used if the direction of conveyance is directed downwards.
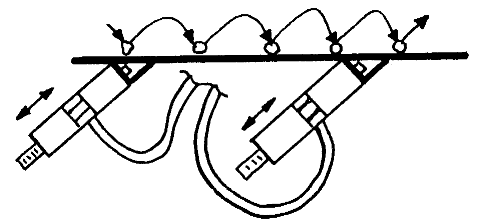
Transportation of materials
1.2.2. Remarks
Please note for all types of vibrators due to handling and application:
The natural frequency of materials, silos, channels, etc. can be calculated theoretically. These calculations will rarely correspond with reality.
Tables or calculations assist the selection and positioning of the vibrator. However, the optimum setting of the vibrator should be found by testing. You will find some basic formulas and tables in the chapter "Selection of the vibrator."
In order to find the optimum setting of the vibrator, it is necessary to connect a compressed air regulator or a needle valve with the vibrator to regulate the air volume and the air pressure.
The knowledge about the natural frequency of the material to be conveyed, to be compressed or to be separated helps with the setting of the vibrator
The frequency range of the vibrators varies from 2000 to over 20,000 min-1 or from 35 to 350 Hz. The information in the technical data sheet is determined when the vibrator is mounted on a laboratory test block.
Often the natural frequency of the material is outside the possible vibration frequency of the selected vibrator. In this cases, please select a more poweful vibrator.
It is recommended to choose a vibrator which achieves the best possible results at operating with 75% of its full power. So that even after years despite abrasion, corrosion, etc. the power (beat frequency) of the vibrator can still be increased for a further optimal result.
Note: The pneumatic vibrators should not be operated with pressure higher than 7 bar (100 psi).
 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Nederlands
Nederlands

![[Translate to Englisch:] [Translate to Englisch:]](/fileadmin/user_upload/Neue_Bilder_2022/Headerbilder/Header.jpg)